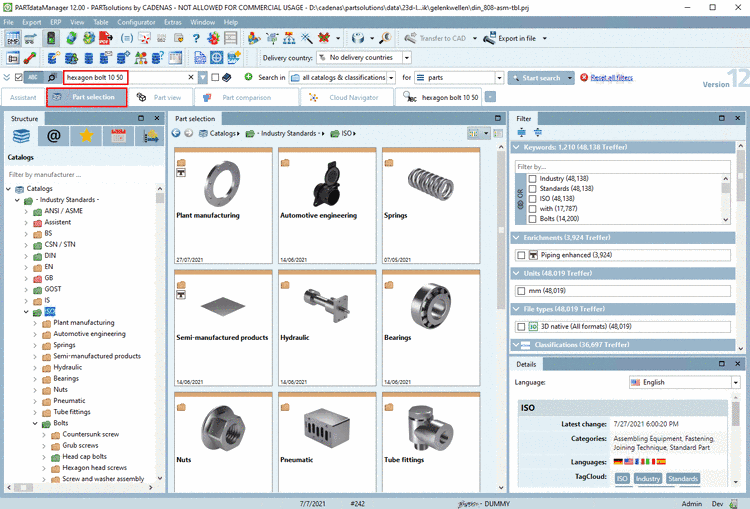
As of V11 SP9 a specific Piping Classification is provided. When exporting classified products respective data will be available in the CAD model (e.g. for technical design).
Product data provided on port level by classification:
Pipe Connector Function: Flow direction of medium or fastening
Pipe Connector ISOGEN Code: ISOGEN code for the part (4 letters)
Reference Guide: https://docs.hexagonppm.com/reader/0lruBS_9RMe3GCYewUDFLw/jzNMOLyC0egjVBNRXD5wrg
Between ISOGEN Code and VDI Form Code there are some overlaps.
Between ISOGEN Code and VDI Form Code there are some overlaps.
For pipes, the following connection forms are distinguished by means of appropriate codes (the zero points of the connection coordinate systems lie on the connection points marked with a circle).
List field selection: e..g. NIPP, MUFF, GLAT, RUF, OVFL (see VDI 3805)
Connection forms for air ducts
For air ducts, the connection forms are distinguished by means of appropriate codes (the connection points are marked by a small circle in each case).
The connection method is determined by an alphanumeric code which defines the qualitative form of the active area pairing in the connection. It can be made up of, e.g., a DIN number for the type of thread or flange, combined with a pressure stage or rating provided that the latter has an impact on the form of the active area (e.g. in the case of flanges).
Examples: DIN 13-1 Metric thread, DIN 103-2 ISO-trapezoidal thread, metric, DIN 2501 Flange PN10, etc.
Pipe Connector Nominal Diameter: Nominal (inner) pipe connector diameter.
Pipe Connector External Diameter: External pipe connector diameter, controlled by respective variable
Intelligent Piping Ports and Anchor ports (NX), which enable direct integration
Existing pipe strings are directly resolved and the inserted products directly integrated.
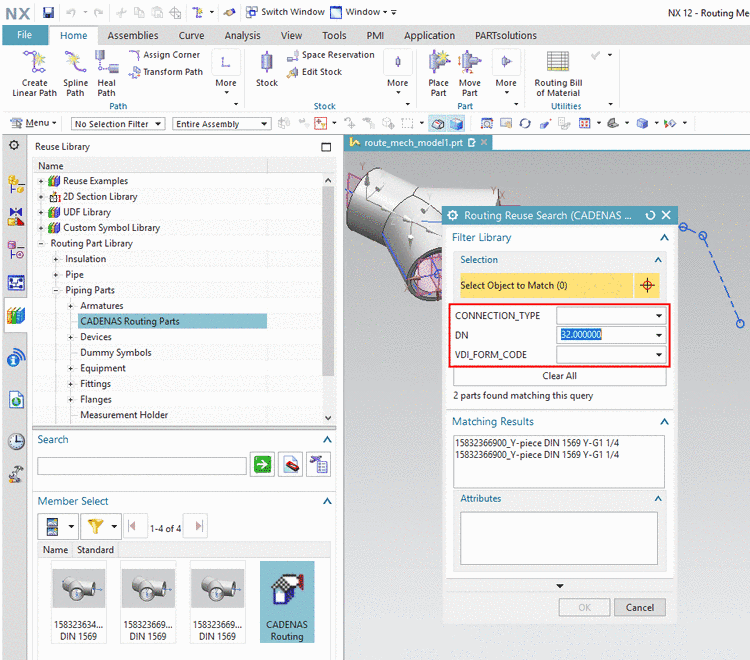
All parts exported from PSOL to NX are stored in a separated CADENAS Routing Parts Library. The parts behave in the same way as products created in the native library. They can be dragged into the opened part directly via Drag & Drop.
When dragging the "CADENAS Routing" node into the assembly, the dialog box Routing Reuse Search (CADENAS Routing Parts) is opened and you can filter the library parts by choosing values in the different list fields.