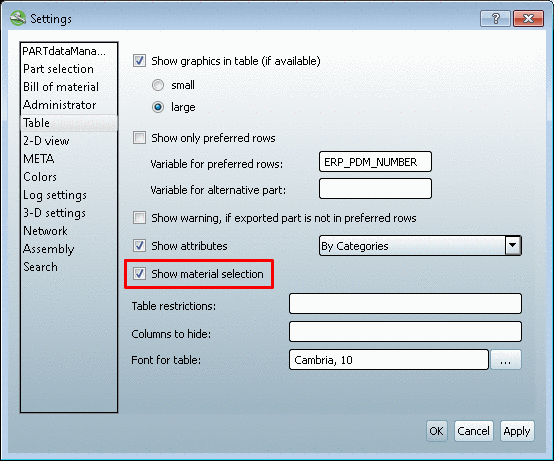
As of V12 there is a new function Automatic Class Mapping: Edit....
An important difference in compare to function Map class systems is, that it's a virtual mapping here, so that the mapped classes and attributes are transferred into the target systems during export, but classification data is not written into the project files physically.
In the following example, a class attribute of the CNS classification shall be mapped to a class attribute of the eClass 9.1 classification. That means, beginning in the upper table (Mapping between classes), class data is entered and then attribute data in the lower table (Mapping between characteristics).
In the upper table, click on
 Add System.
Add System.-> The same-named dialog box is opened.
With the exact wording in lower case, enter the name of the desired classification and confirm with .
Target System: With exact wording, in lower case, enter the name of the desired classification and confirm with Enter.
Target Class: Open the list field and select the desired class.
Number: By default, one instance is created. However, you can create multiple instances of the class.
Bidirectional: By default, mapping only takes place in the stated direction. When activating this option, there is a mapping from Origin Class to Target Class and the other way round.
Copy features: All identical attributes are copied. This option excludes entries in the lower table.
Copy mapped features (default): Only those attributes are mapped, which have been stated in the lower table explicitly.
With exact wording in lower case, enter the name of the desired classification and confirm with .
Origin Class: Open the list field and select the same class as in upper table. Alternatively, you can use the wildcard symbol (*), (which affects the performance negatively.)
Origin Characteristic: Open the list field and select the desired attribute.
Target System: With exact wording in lower case, enter the name of the desired classification and confirm with Enter.
Target Class: Open the list field and select the desired class.
Target Feature: Open the list field and select the desired attribute.
Copy Characteristic Name ("Copy Variable Name"): Select this option, if a certain variable shall be mapped.
Copy Characteristic Value: Select this option, if a fixed value shall be mapped.
Value Mapping (optionally): Click on the button
 , if you want to adjust the original
value.
, if you want to adjust the original
value.-> The same-named dialog box is opened.
With entries under Original Value and Target Value, you can adjust the target value. After confirming with , the button looks like this
 .
.Objective Unit (optionally): If a unit is stated, a conversion of the value is automatically performed.
Execute the mapping by clicking .
Main features are the "table area" at the top (for Class Mapping) and the "table area" at the bottom (for Attribute Mapping).
Each "table area" has 2 tabs, one for Mapped elements and one for Suggested items. These are separate tables with separate data.
Each "table area" has it's own buttons. They work on the current active tab.
Buttons top right of the tables
 Add System: Adds
a source system (e.g. eclass8.0, eclass8.1, etc...). (No duplicates
possible).
Add System: Adds
a source system (e.g. eclass8.0, eclass8.1, etc...). (No duplicates
possible). Add Item: Adds a
new element under a Top Node with empty data and default values.
Add Item: Adds a
new element under a Top Node with empty data and default values.Element is inserted at last position under current selected Top Node or current selected element.
 Remove: Deletes the
current selected Element or Top Node (also works with Del-key on
keyboard).
Remove: Deletes the
current selected Element or Top Node (also works with Del-key on
keyboard).When deleting a Top Node all elements under the Top Node will be deleted, too. So there is a dialog for asking the user if he really wants to delete it.
Each "table area" has it's own search bar which searches for all source and destination data (system and class (and variable and id when searching in Variables)).
Import eClass XML: Imports eClass Data from a directory with suitable .xml files (legacy case).
Import eClass CSV: Imports eClass Data from a directory with suitable .csv files. (Upgrade to next eClass Version).
import CSV: Imports Data from a directory with suitable .csv files. (e.g. eclass8.0_classes_mapped.csv).
Export CSV: Exports the Data from the tables to a directory in several .csv files (like Import-Format above).
The exported csv files are separated by classification system, class data / variable data and mapped / suggested (e.g. eclass5.1_classes_mapped.csv or eclass5.1_variables_suggested.csv).
When importing data (via .csv files), duplicates are removed (may take some time).
When exporting data (via .csv files), duplicates are removed (only changed Elements will be checked).
When saving data (via button) duplicates are removed (only changed elements will be checked) and Variable Mapping Data is checked for missing corresponding Class Mapping Data. If elements are found, a dialog appears where either missing Class Mapping Data can be added or wrong Variable Mapping Data can be deleted.
Normally the table cells are editable strings or checkboxes.
Some cells give you a List of possible string values, when clicked (e.g. source class if source system is existing).
In the table Mapping between characteristics, in the column Value Mapping, in the respective table cell, a button
 (
( ) opening a special dialog is found. Here, source
values (possibly multiple) can be mapped to target values (warning, if
it is a duplicate). That means, in the mapped variable the value is
changed or the fixed value is changed.
) opening a special dialog is found. Here, source
values (possibly multiple) can be mapped to target values (warning, if
it is a duplicate). That means, in the mapped variable the value is
changed or the fixed value is changed.Objective Unit: If the field is enabled, the unit will be converted. If there are values, they are automatically converted into the new unit.
There are classes without attributes. In this case, entries in the lower table are obsolete. The reverse case is not possible. The upper table always has to contain entries.



![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/fr/installation_ecatalogsolutions/doc/images/note.png)