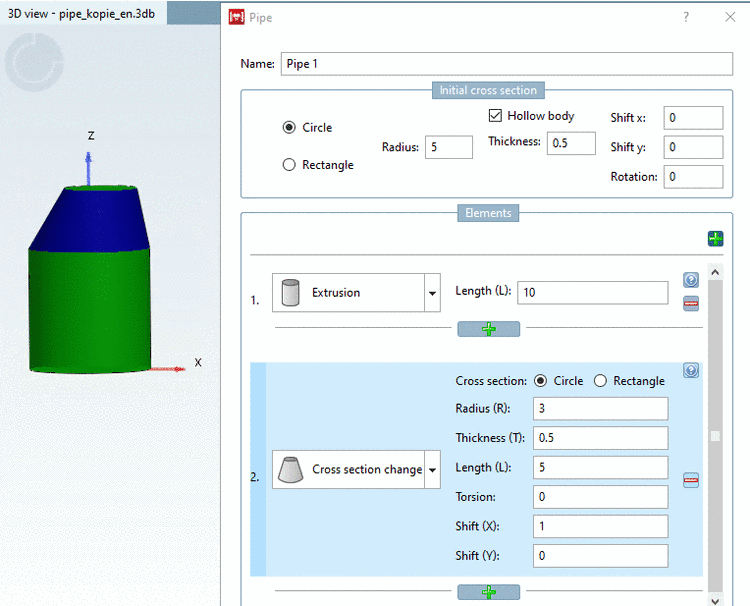
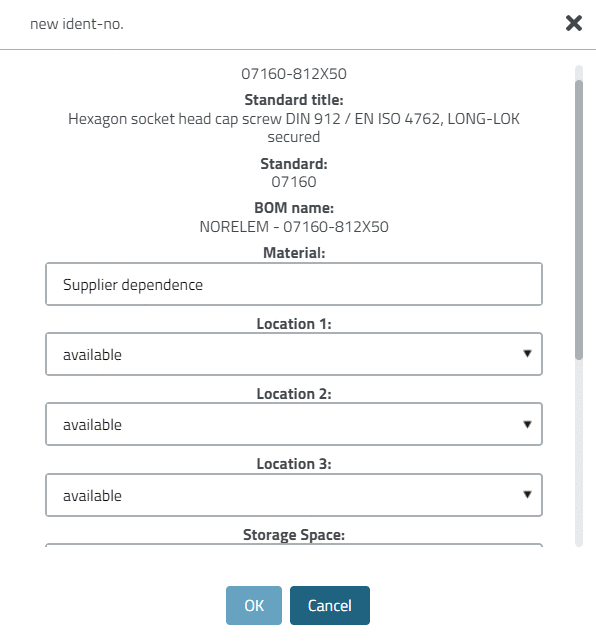
In the Elements section, the pipe run can be specified.
Error icon
 : This icon and its associated label shows if
and in which of the elements an error occurred.
: This icon and its associated label shows if
and in which of the elements an error occurred.Element: Single element of the pipe run. A pipe consists of at least one to unlimited elements (theoretically unlimited -> RAM does limit the count). Further information for each element type will follow.
Add new operation below.
 (not visible in above figure)/ Delete this operation.
(not visible in above figure)/ Delete this operation.
Remove all operations.
 : Since a pipe needs to consist of at least
one element, there will be one empty element left.
: Since a pipe needs to consist of at least
one element, there will be one empty element left.Help
 : Technical drawings will help to correctly
fill the single input fields.
: Technical drawings will help to correctly
fill the single input fields.
Every input field in the group (exceptions will be mentioned) allows table and/or local variables and expressions (only PARTdesigner usual expressions, see Section 14.1, “PARTdesigner-Expressions ”). If variables are used, the error detection is limited to the current value of the variable. Some constellations of the variable values could result in an invalid part, but validating each possible variable constellation could lead to immense computation.
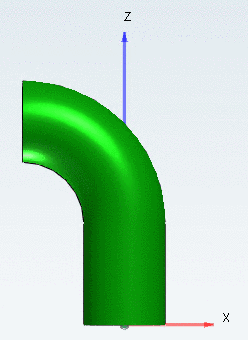
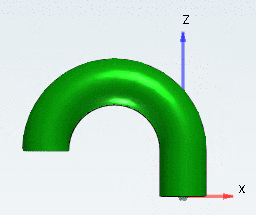
Smooth bend will create a rotation body.
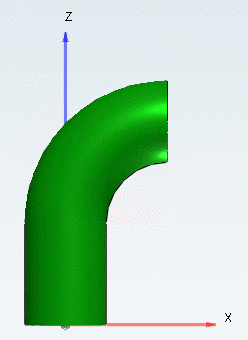
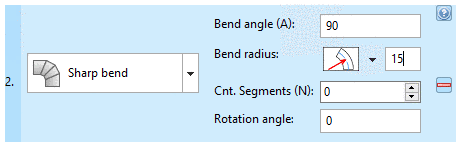
Bend angle (A): Enter an angle to describe how far the pipe should bend in this element (segment of a circular arc). Any values between 0° and 360° are valid.
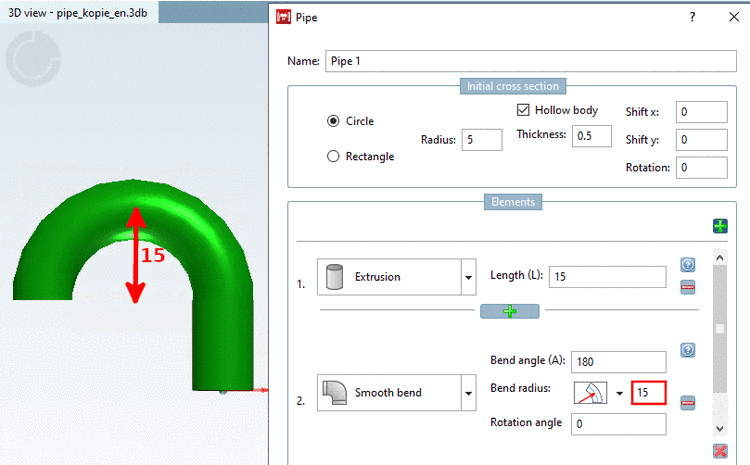
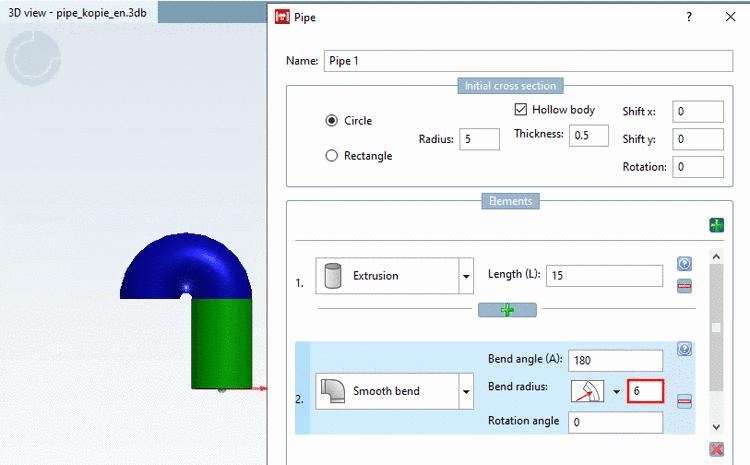
Bend radius: Enter the bend radius of the pipe.
Toggle for radius reference point: With a click on the arrow you can open a list field where you can switch between different modes:
Rotation angle: Specify the angle for the orientation of the pipe run. Enter any value (360° will be equal to 0° and so on).
The elements Sharp bend and Smooth bend are similar, however, Sharp bend is built from straight pipe elements connected under a certain angle (in practice mostly welded).
Bend angle: Enter an angle to describe how far the pipe should bend in this element (segment of a circular arc). Any values between 0° and 360° are valid.
Bend radius: Enter the bend radius of the pipe.
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/it/partwarehouse/doc/images/note.png)
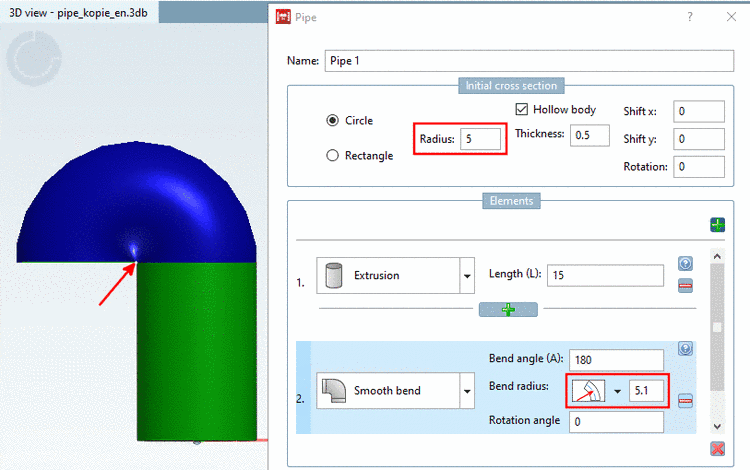
Note The radius anchor point needs to be outside the geometry.
With bend radius mode
 Center radius (Rc) a circle with a radius of
needs to have a value greater than 5. This gets more
complicated for rotated rectangles, but here again
the error detection
Center radius (Rc) a circle with a radius of
needs to have a value greater than 5. This gets more
complicated for rotated rectangles, but here again
the error detection  will help and point out if
the radius value is too small.
will help and point out if
the radius value is too small.Toggle for radius reference point: With a click on the icon, you can switch between different modes:
No. segments: The number of pipe-parts used to approach a circle. This field does not allow variables or expressions.
Rotation angle: Define the angle for the orientation of the pipe run.
Valid values depend on the cross section type. For type Circle any value is valid. For type Rectangle values are limited to 0°, 90°, 180° and 270° due to the restrictions given by the need to be backwards compatible.
The element Cross section change allows changing the shape and/or alignment of the cross section. Therefore, the incoming cross section and the out coming cross section could differ. This will affect all the following elements.
Cross section: Select the cross section type (Circle / Rectangle).
Radius (R) (Cross section dimension): Define the size of the new cross section.
Thickness (T): Only active if the whole pipe is hollow (see Fig. „ Initial cross section -> Circle “), if so a value needs to be given.
Torsion: Rotation of the cross section plane around its center. The value is limited to a maximum of 180°. However high values do result in strange bodies so keep an eye on the result and in doubt split this element into two sweep elements with half the length and half the torsion each.
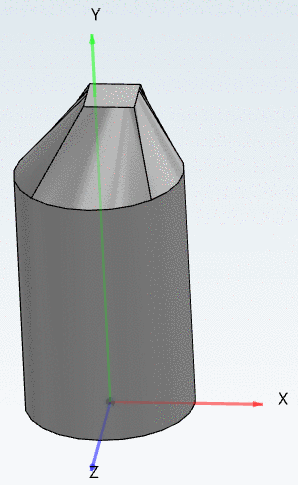
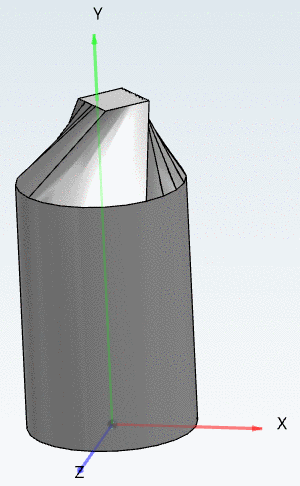
The following example shows sweeps with rectangle cross sections.
Displacement: (Translation X / Translation Y) Add values to create an eccentric cross section at the element end.
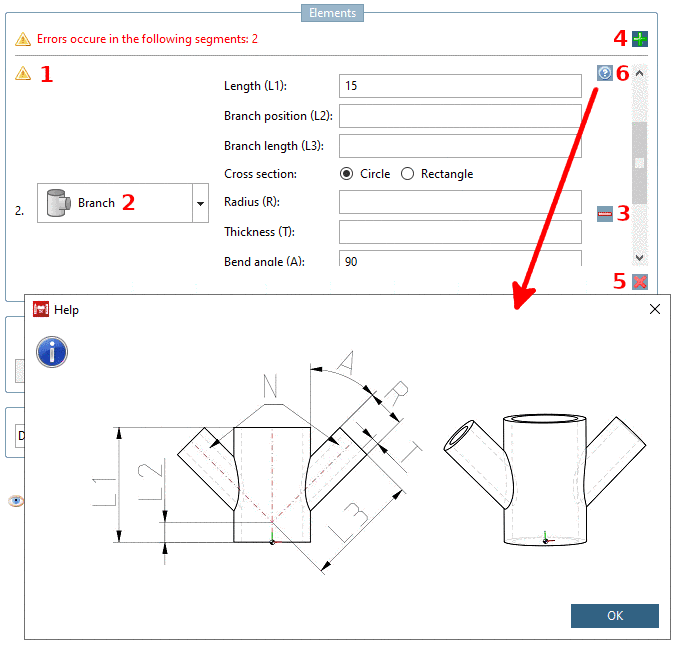
The element Branch allows attaching separate branches to a pipe. Therefore, add a branch element to a pipe and select the count and shape of the branches. Later new pipes can be attached to each branch.
Length (L1): Length of the main branch..
Branch position (L2): Position of the side branches
Branch length (L3): Length of the side branches.
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/it/partwarehouse/doc/images/note.png)
Note The value should be at least half the size of the diameter of the main branch (incoming cross section). (Not visible) start point of a side branch is in the center of the main branch. If the value is greater than the radius of the main branch, it is assured that the side branch stands out from the main branch.
Cross section (Circle / Rectangle): Select the cross section type of the side branches.
Specify Radius (R) and Thickness (T) of the side branches. The input field under Thickness (T) is only enabled if under Initial cross section the option Hollow body is enabled.
Bend angle (A) represents the angle between the main branch and its side branches. By default this is set to "90" that results in an T-shaped branch.
Rotation: Defines the angle for the direction of the first side branch (Default 0° matches the direction of X axis.)
Cnt. Branches (N): Defines the number of side branches. The side branches will be equally distributed around the main branch. This field does not allow variables or expressions.
Information on how to edit the pipe at branches can be found under Section 7.6.2.9.4, “Context menu commands” -> Branches.