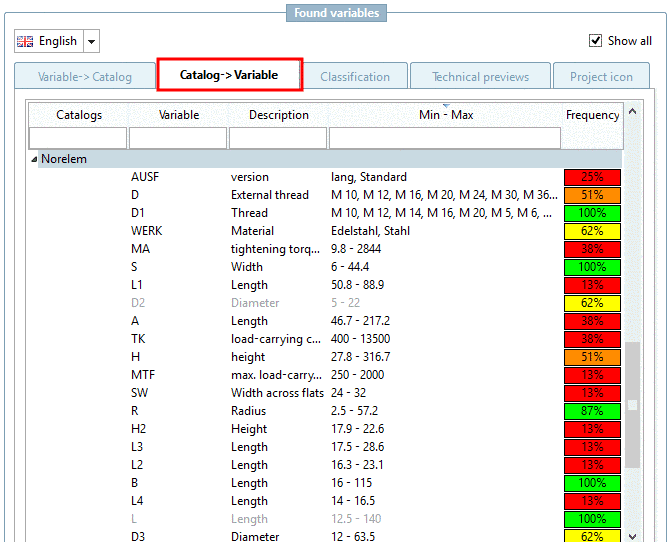
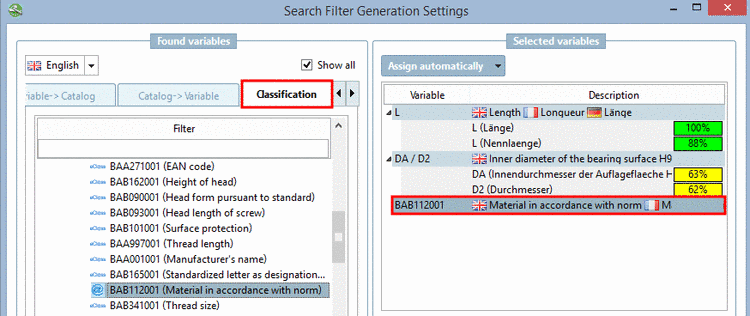
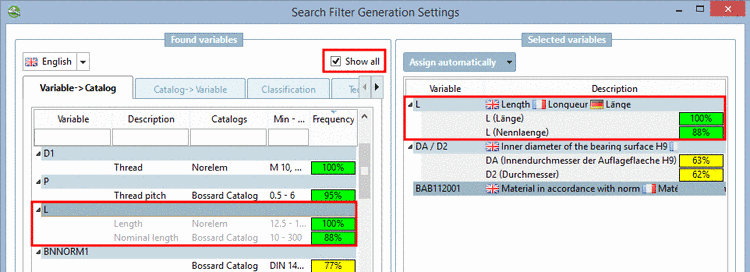
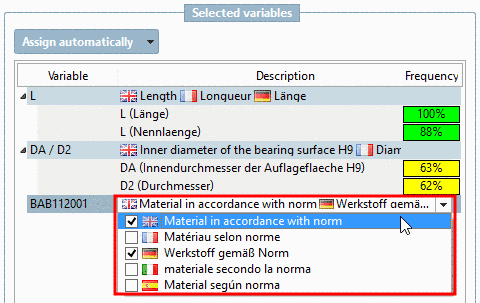
Classification according to CNSORDERNO or CNSTYPECODE?
CNSORDERNO = Order number (article number)
Order number is partly used for products with value range fields (yellow fields).
But Order number is also used for products without value range fields (yellow fields).
Common product groups are: Brackets, switches, bolts, nuts, but also more complex parts.
Characteristic feature in both cases is that there is no strict relation between table values and parts of the order number. This is the essential difference in compare with CNSTYPECODE. See Fig. „Example: Clear relation between parts of type code and single variable values“.
CNSTYPECODE = Typenschlüssel (Article code / order code)
Type code is partly used for products with particularly complex set of rules. In these cases the project has value range fields (yellow fields), whereby mostly a huge number of combination possibilities results.
Common product groups are: Cylinders, motors, gears, linear modules, if configurable and customizable.
But Type code can also be used for products without value range fields.
Characteristic feature in both cases is that there is a strict relation between table values and parts of the type code.
Enter article number in eCATALOGsolutions correctly
Hidden variables can also be used for a mapping. The variable is considered when indexing and can be searched.


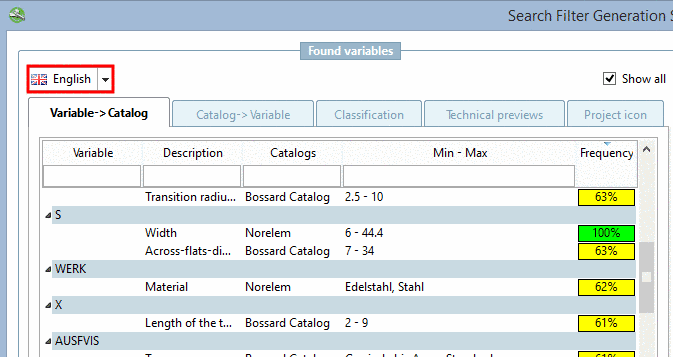
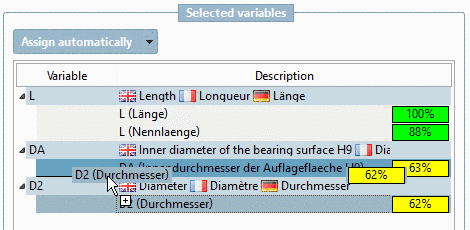
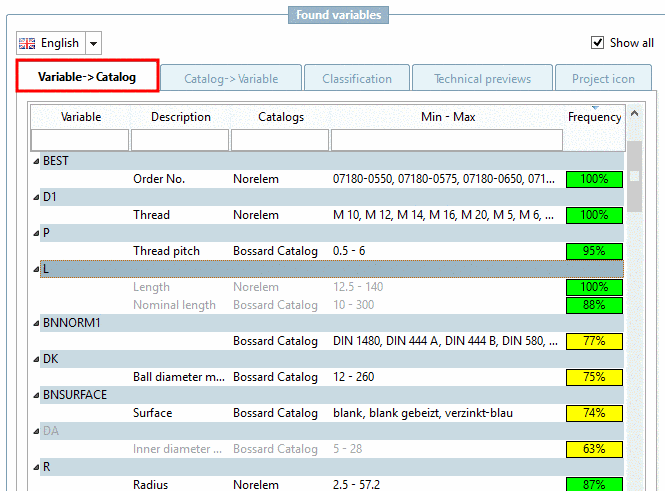
![[Note]](https://webapi.partcommunity.com/service/help/latest/pages/en/partsolutions_user/doc/images/note.png)